I think anyone who really a car fans will have a favorable impression on the Mazda brand. Not only because Mazda has participated in the 24 Hours of Le Mans for more than ten years, but also became the first Asian manufacturer to win the championship. It is also because of the focus on the Uncommon discipline of “Rotor” for nearly half a century and has successfully created many very popular classic models. Of course, all kinds of Mazda that appear in animation, movies, and racing are also examples of the model to attract fans with strength. Behind Mazda’s popularity among fans and continuous technological breakthroughs is the generation of Mazda’s obsession with outstanding products.
Rotor forty-seven warriors who steady the overall competition situation of Japanese domestic auto market.
The story begins in the early 1960s. In the early 1960s, Japan’s domestic auto market was highly competitive. For Mazda, to become a leader in the automotive market means to deeper the development of technology and comprehensively enhance product competitiveness. At that time, President Matsuda Tsuneji believed that “to survive, the company must master unique technology.” Mazda has invested a lot of research and development resources to achieve the practical use of the rotor engine. However, the road to practical use is bumpy.
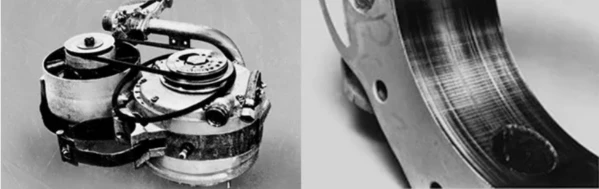

To fully grasp the technology of Wankel’s Rotor engine, Mazda’s technicians specially studied from the NSU company of West Germany. At the time, there were still problems with friction inside the engine that could not be solved. In order to mass-produce the rotor engine, this problem must be solved. So Mazda brought together 47 technical elites to quickly set up the Rotor Engine Research Department to focus on this issue.


The automotive industry and research institutes have questioned the practicality of rotor engines. Even the inside company has ridiculed “a waste of budget”. Despite bore with all the torment of uneasiness and anxiety, these technical elites have consistently believed that one day they will usher in the practical use of the rotor engine and continue to work hard for it.
Finally, an engineer proposed a method of punching a cross hole at the top of the rotor seal to change its frequency characteristics to eliminate friction marks. After testing, this method worked. Since then, Mazda’s rotor engine has developed by leaps and bounds on the road to practical use. On May 30, 1967, the first Cosmo Sport with a rotor engine was introduced. Mazda is the only company to mass-produce a rotor engine. The 47 engineers who laid a solid foundation for the rotor engine were also referred to as Akōrōshi by engine research minister Yamamoto Kenichi. Known to history as the rotor forty-seven warriors.
The first generation – SKYACTIV


With the change of times, car manufacturers have gradually begun to pay attention to the new topic of “environmental protection.” Helpless, the rotor engine can only be temporarily put into the museum by Mazda. However, manufacturers with real technical strength will not be restricted by mega-trends. SKYACTIV is a great example.
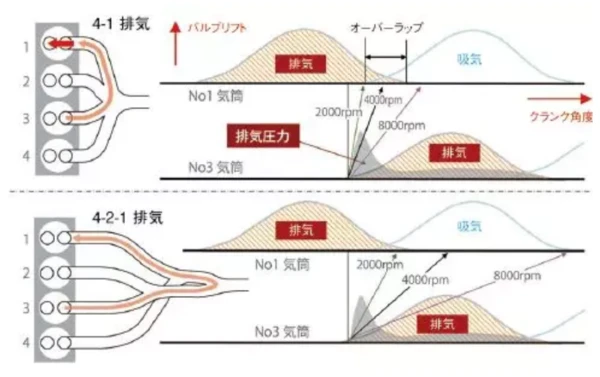

When other manufacturers rely on small-displacement turbocharging to achieve energy-saving emission reduction, Mazda chose a “difficult road” that digging deep into the potential of naturally aspirated engines, using a method of increasing compression ratio and improving thermal efficiency to achieve a cleaner and more efficient internal combustion engine. Before the advent of the SKYACTIV-G engine, most people still knew that high-compression engines could only use high-grade gasoline. Because of the high compression ratio and the need for better anti-knocking gasoline. But Mazda engineers have reduced knocking at high compression ratios by using a 4-2-1 exhaust system to reduce residual gases and reduce burn time. This makes it possible to use 92# gasoline at a high compression ratio of 13:1. At the same time, the fuel economy is increased by 15% with a 15% increase in torque in the low and medium speed range.
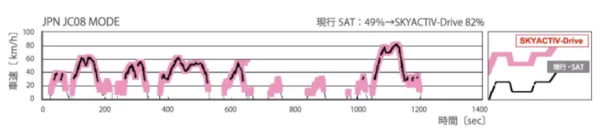

Of course, in order to achieve smooth and efficient operation quality, it is also necessary to need the help of the SKYACTIV-Drive gearbox. The 6-speed SKYACTIV-Drive gearbox, which can achieve 82% full-speed domain locking, not only has first-class power response speed but also achieves a smooth-shifting action through the new mechatronics control unit. You can’t just listen to me, you have to drive it yourself to feel the same.
Creating the era – SKYACTIV-X


When everyone was still immersed in the fragrance of SKYACTIV technology, Mazda added a fire to everyone’s enthusiasm the year before – Mazda will manufacture a compression-ignition gasoline engine. A diesel-like ignition mode is ported to a gasoline engine. Is this really achievable? Yes, SKYACTIV-X is the answer.


SKYACTIV-X is the world’s first new generation of SKYACTIV gasoline engine equipped with “Spark Controlled Compression Ignition (SPCCI)” technology. It is the development goal of Mazda’s second phase and a milestone product in the pursuit of an ideal internal combustion engine. This engine combines the high standard emission advantages of a spark-ignition engine with the innate fuel economy and excellent initial response performance of a compression ignition engine.
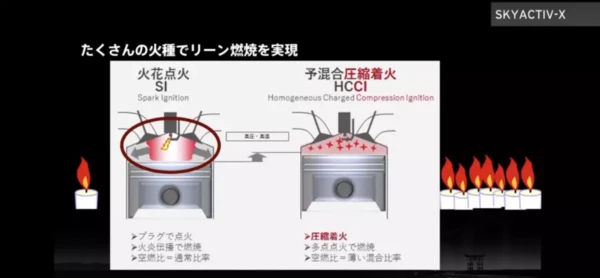

But why should Mazda bring the way of compression ignition to the gasoline engine? Because it is efficient. Compression ignition can burn the gas in all corners of the combustion chamber in a very short time after the piston starts moving from top dead center. It can squeeze the piston strongly and persistently to improve combustion efficiency. And the way of compression ignition igniting theoretically requires only half of the fuel to achieve the same effect as ignition combustion, because the ignition mode of compression ignition can provide an air-fuel ratio that is not possible with spark ignition. In layman’s terms, when the SKYACTIV-X engine starts running, it is first ignited by the spark plug to expand the fireball. Just like the second piston (air piston), it continues to compress the mixed gas in the combustion chamber to create the environment needed for compression ignition. By controlling the occasion of ignition of the spark plug, the compression ignition is expanded, and smoothly realize its switching with spark ignition. So that fully controllable compression ignition and spark ignition can be realized.
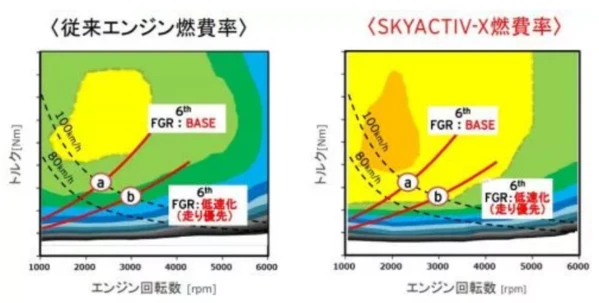

Based on the 2.0L displacement, the new engine achieves a minimum of 10% and a torque increase of up to 30% in the full speed range compared to the current SKYACTIV-G. At the same time, it can also exert the initial response-sensitive acceleration performance of diesel engine without throttle. Compared with the MZR engine in 2008, the fuel economy has improved by 35% to 45%, achieving fuel economy equal to or higher than that of the current SKYACTIV-D diesel engine. In this way, it is basically possible to use a 2.0-liter displacement to achieve a 2.5-liter power experience while sitting at 1.5 liters of fuel economy.
More than focusing on the engine
The above crystallization of the wisdom of Mazda engineers is actually to give drivers a better experience, so that they really feel the joy of drive. However, now is already 2019, and some black technologies such as “compression ignition gasoline engine” have been developed. They should exploring further. This time, the engineers focused on the body structure.
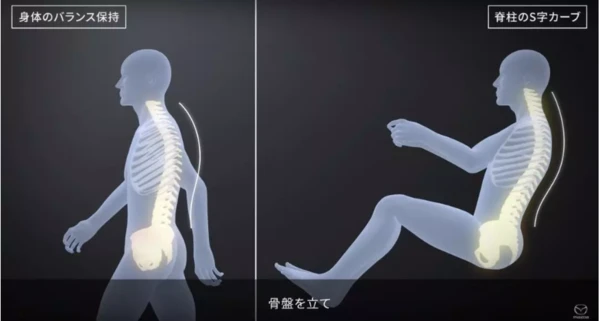

Under the guidance of the people-oriented concept of car, Mazda created the SKYACTIV-VEHICLE ARCHITECTURE. The engineers took inspiration from the human walking posture and realized the advanced ability of the human being to maintain the balance. This discovery led them to think about whether they could create the ideal state of a car, so that even when driving a car, the occupants could play the same balance of human ability as they did when they walked. That is to say, when driving a car, the seat can make the pelvis stand upright and keep the spine in a S-shaped curve, thus replacing the support of the human lower limbs, while smoothly transferring the force from the road surface to the pelvis, keeping the pelvis continuous and stable motion.

In order to maximize the ability of humans to maintain balance while riding, Mazda engineers chose three aspects to start. The first is the design of a new ergonomic chair that allows people to keep the pelvis upright while riding while maintaining the S-curve of the spine. And also adjust the rigidity of the seat cushion and the cushion spring, so that the force can be transmitted linearly from the upper part of the spring to the human body.
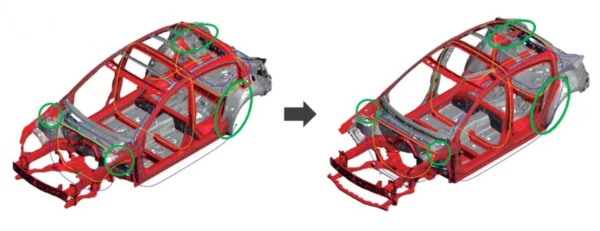

Secondly, the body is adjusted to maximize the sense of the road to the driver. The body is based on a traditional ring structure, connecting the upper, lower, left and right skeletons, and adopting a multi-directional annular structure to connect the skeleton in the front-rear direction, thereby improving the four-wheel diagonal rigidity. Engineers also combine multi-directional annular construction with ultra-high tensile steel plates based on the concept of basic skeleton linearization and continuous, achieving a win-win effect of weight reduction and rigidity improvement at a higher level.


Finally, the parts of the suspension are redesigned to make the road sense deliver to the driver smoothly, including the use of a spherical bushing between the suspension arm and the connecting rod and the strength of the tire sidewall.
All in all, Mazda is following this path along the way to achieving a better control experience. Based on the constant innovation of the basic performance of the car, it brings the most cutting-edge technology to consumers and also shows its technological strength to the world. I believe that as long as Mazda is there, human beings will not be bored in the pursuit of car ideals.

